 |
Pore-forming proteins and host-pathogen interactions
Crystallography and ISMB
Birkbeck College London | 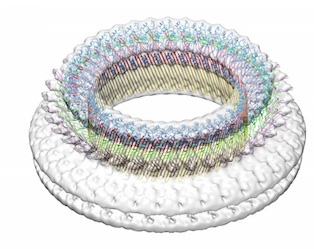 |
Helen Saibil,
Natasha Lukoyanova, Natasha
Dudkina, Katja Ota, Andrea Nans, Vicky Hale, Jean Watermeyer
Former group members Sarah Tilley, Selda Bahrdt-Genisyurek
Collaborators:
Peter Andrew (University of Leicester), Joe Trapani and Ilia Voskoboinik
(Peter McCallum Cancer Centre, Melbourne),
James Whisstock , Michelle Dunstone (Monash University), Richard Hayward (ISMB), Mike Blackman (NIMR/Crick Institute), Roland Fleck
(Kings College London)

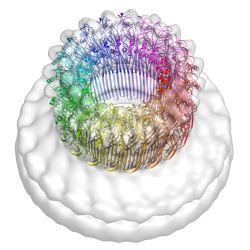
Steps in pore formation by pneumolysin
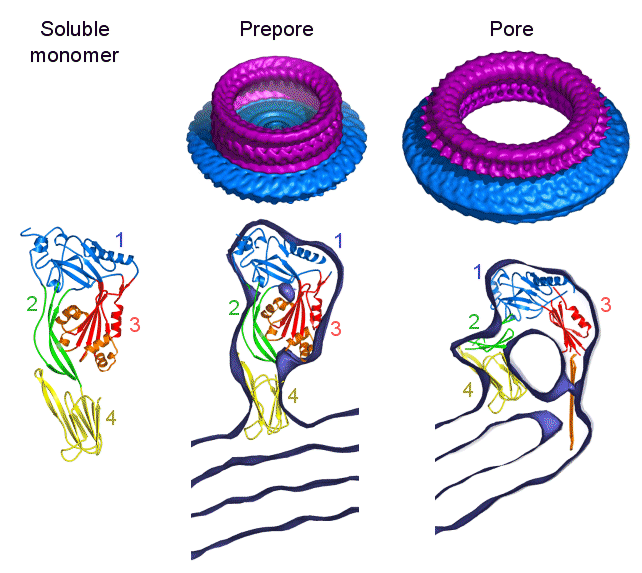
The pore-forming toxin pneumolysin is a member of a large family of
highly conserved, cholesterol binding toxins. These toxins are released
from gram positive bacteria as soluble monomeric proteins, which then assemble
into prepore oligomers on the surface of cholesterol-containing cell membranes.
The prepores then puncture the membrane to form very large pores containing
30-50 subunits, with a channel diameter around 250 Angstroms. The
structures of the soluble form
of two members of the family, perfringolysin and intermedilysin, have been determined by X-ray
crystallography
(Rossjohn et al, 1997, Cell 89, 685-692; 1PFO; Polekhina et al, 2005, PNAS 102, 600-605; 1S3R).
We have been studying oligomeric forms of pneumolysin bound to liposomes by
cryo EM, image processing and atomic structure docking using the domains
of perfringolysin. In the 3D surface views (top), the protein rings are shown in purple and the surrounding liposome
membrane in blue. The sections through the maps show the fitted domain structures. The work has been funded by the BBSRC.
References
Subunit organization and symmetry of pore-forming, oligomeric pneumolysin. Morgan, PJ, Hyman, SC, Rowe, AJ,
Mitchell, TJ, Andrew, PW & Saibil, HR (1995) FEBS Letters 371, 77-80.
Two structural transitions in membrane pore formation by pneumolysin,
the pore-forming toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Gilbert, RJC,
Jimenez JL, Chen, S, Tickle, IJ, Rossjohn, J, Parker, M, Andrew, PW
and Saibil, HR (1999) Cell 97, 647-655.
Structural basis of pore formation by the bacterial toxin pneumolysin. Tilley, SJ, Orlova, EV, Gilbert, RJC,
Andrew, PW & Saibil, HR (2005) Cell 121, 247-256.
The mechanism of pore formation by bacterial toxins. Tilley, SJ & Saibil, HR (2006)
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 16, 230-236.
| Friend or foe: the same fold for attack and defense. Lukoyanova, N &
Saibil, HR (2008) Trends Immunol. 29, 51-53. | 
|
| The molecular basis for perforin oligomerization and transmembrane pore assembly.
Baran K, Dunstone M, Chia J, Ciccone A, Browne K, Clarke C, Lukoyanova N, Saibil H, Whisstock J,
Voskoboinik I, Trapani J (2009) Immunity 30, 684-95. |
| The structural basis for membrane binding and pore formation by
lymphocyte perforin. Law, R, Lukoyanova, N, Voskoboinik, I, Caradoc-Davies,
TT, Baran, K, Dunstone, MA, D'Angelo, ME, Orlova, EV, Coulibaly, F, Verschoor,
S, Browne, KA, Ciccone, A, Kuiper, MJ, Bird, PI, Trapani, JA, Saibil, HR &
Whisstock, JC (2010) Nature 468, 447-451. |
 |
| Stepwise visualization of membrane pore formation by
suilysin,a bacterial cholesterol-dependent cytolysin. Leung, C, Dudkina, NV, Lukoyanova, N, Hodel, AW, Farabella, I, Pandurangan,
AP, Jahan, N, Damaso, MP, Osmanovic, D, Reboul, CF, Dunstone, MA, Andrew, PW, Lonnen, R, Topf, M, Saibil, HR, Hoogenboom, BW (2014)
eLife 3:e04247 | 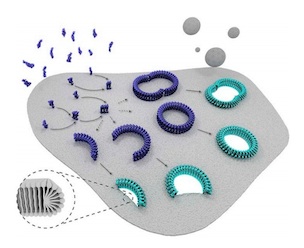 |
| Conformational changes during pore formation by
the perforin-related protein pleurotolysin. Lukoyanova, N, Kondos, SC, Farabella, I, Law, RHP, Caradoc-Davies, TT, Spicer, BA,
Kleifeld, O, Traore, D, Ekkel, SM, Voskoboinik, I, Trapani, J, Hatfaludi, T, Oliver, K, Hotze, EM, Tweten RK, Whisstock, JC, Topf, M,
Saibil, HR, Dunstone, MA (2015) PLoS Biol 13:e1002049 |  |
Host-pathogen interactions |
| Chlamydiae Assemble a Pathogen Synapse to Hijack the Host Endoplasmic Reticulum.
Dumoux M, Clare DK, Saibil HR, Hayward RD (2012) Traffic 13, 1612-1627. |
 |
| Pathogen-host reorganisation during Chlamydia invasion revealed by cryo-electron tomography. Nans, A, Saibil, HR,
Hayward, R (2014) Cell. Microbiol. 16, 1457-1472. | |

Birkbeck
Crystallography EM and Image Processing group
Saibil
Home Page








